RECENT PROJECTS
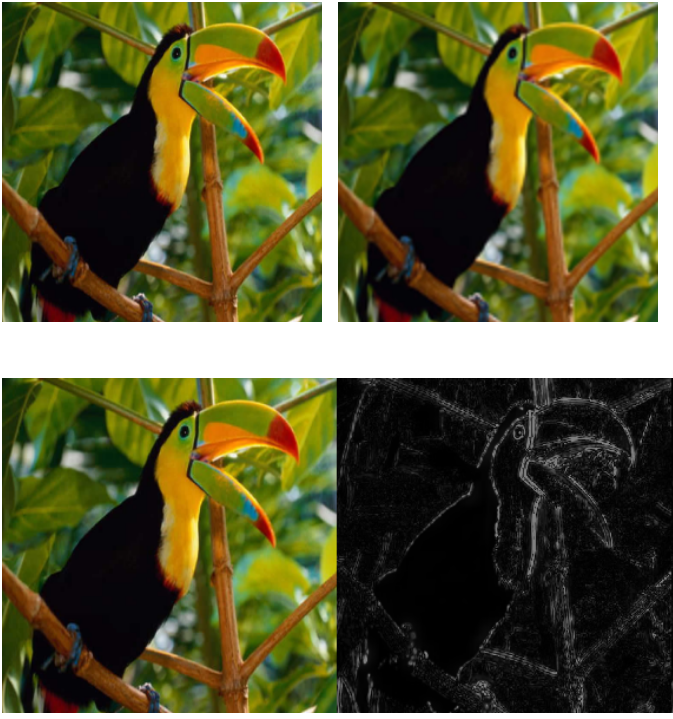
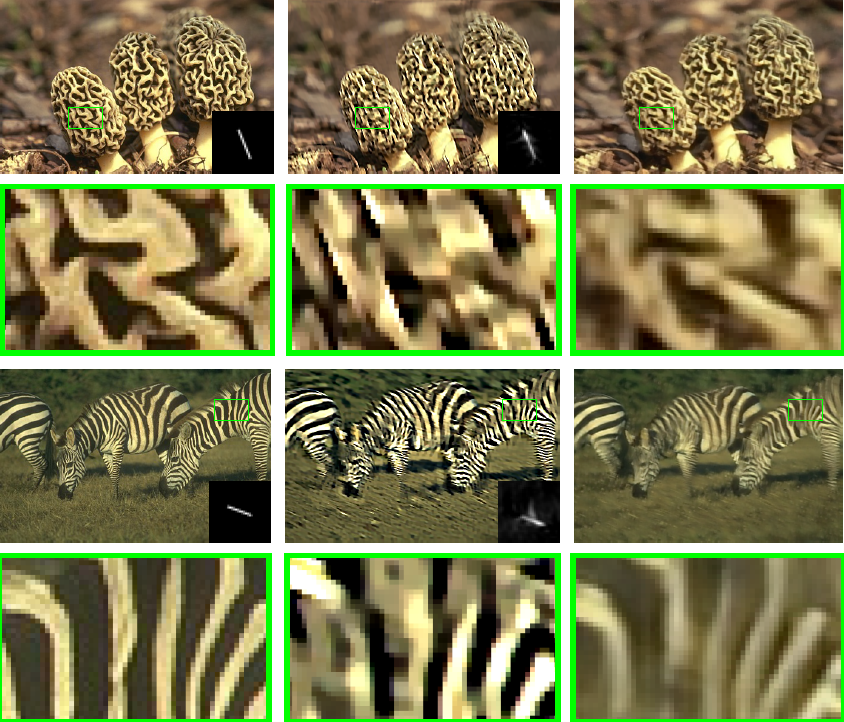
Efficient And Interpretable Deep Blind Image Deblurring Via Algorithm Unrolling
Blind image deblurring remains a topic of enduring interest. Learning based approaches, especially those that employ neural networks have emerged to complement traditional model based methods and in many cases achieve vastly enhanced performance. That said, neural network approaches are generally empirically designed and the underlying structures are difficult to interpret.
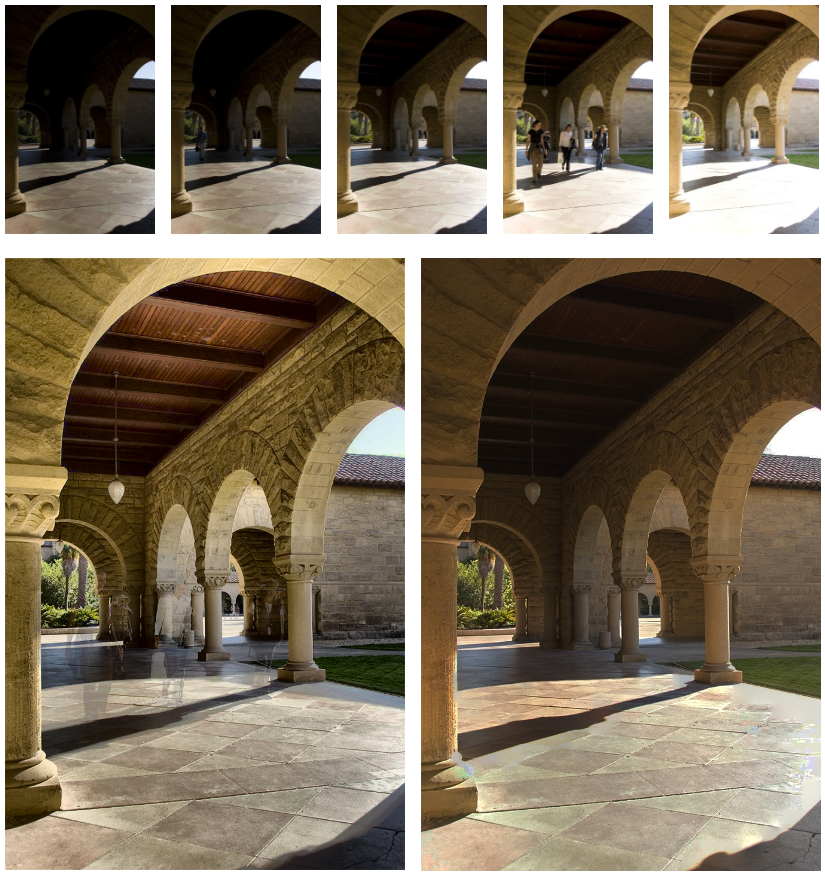
Ghost-Free High Dynamic Range Imaging
We propose a ghost-free high dynamic range (HDR) image synthesis algorithm using a low-rank matrix completion framework, which we call RM-HDR. Based on the assumption that irradiance maps are linearly related to low dynamic range (LDR) image exposures, we formulate ghost region detection as a rank minimization problem.
A MAP Estimation Framework for HDR Video Synthesis
High dynamic range (HDR) image synthesis from multiple low dynamic range (LDR) exposures continues to be a topic of great interest. Its extension to HDR video is also a topic of significant research interest due to its increasing demand and economic costs.
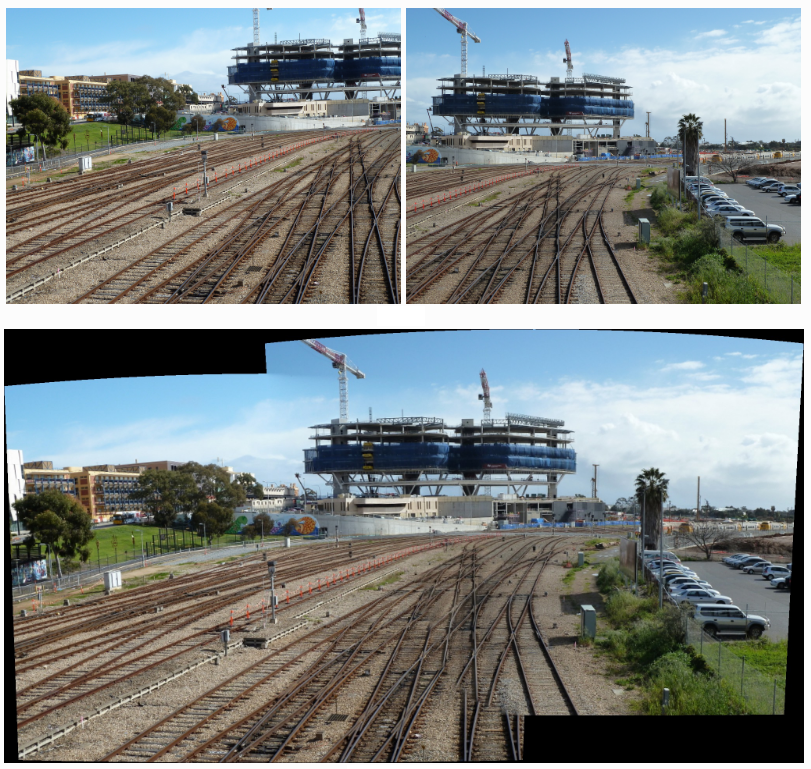
Bundle Robust Alignment for Panoramic Stitching
Here we study the problem of image alignment for panoramic stitching. Unlike most existing approaches that are feature-based, our algorithm works on pixels directly, and accounts for errors across the whole images globally.
Sparsity-based Color Image Super Resolution via Exploiting Cross Channel Constraints
Sparsity constrained single image super-resolution (SR) has been of much recent interest. A typical approach involves sparsely representing patches in a low-resolution (LR) input image via a dictionary of example LR patches, and then using the coefficients of this representation to generate the highresolution (HR) output via an analogous HR dictionary.
Blind Image Deblurring Using Row-Column Sparse Representations
Blind image deblurring is a particularly challenging inverse problem where the blur kernel is unknown and must be estimated en route to recovering the de-blurred image. The problem is of strong practical relevance since many imaging devices such as cellphone cameras, must rely on deblurring algorithms to yield satisfactory image quality.