Deep, convergent, unrolled half-quadratic splitting for image deconvolution
IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging
ABSTRACT
In recent years, algorithm unrolling has emerged as a powerful technique for designing interpretable neural networks based on iterative algorithms. Imaging inverse problems have particularly benefited from unrolling-based deep network design since many traditional model-based approaches rely on iterative optimization. Despite exciting progress, typical unrolling approaches heuristically design layer-specific convolution weights to improve performance. Crucially, convergence properties of the underlying iterative algorithm are lost once layer-specific parameters are learned from training data. We propose an unrolling technique that breaks the trade-off between retaining algorithm properties while simultaneously enhancing performance. We focus on image deblurring and unrolling the widely-applied Half-Quadratic Splitting (HQS) algorithm. We develop a new parametrization scheme which enforces layer-specific parameters to asymptotically approach certain fixed points. Through extensive experimental studies, we verify that our approach achieves competitive performance with state-of-the-art unrolled layer-specific learning and significantly improves over the traditional HQS algorithm. We further establish convergence of the proposed unrolled network as the number of layers approaches infinity, and characterize its convergence rate. Our experimental verification involves simulations that validate the analytical results as well as comparison with state-of-the-art non-blind deblurring techniques on benchmark datasets. The merits of the proposed convergent unrolled network are established over competing alternatives, especially in the regime of limited training.
Code
DECUN
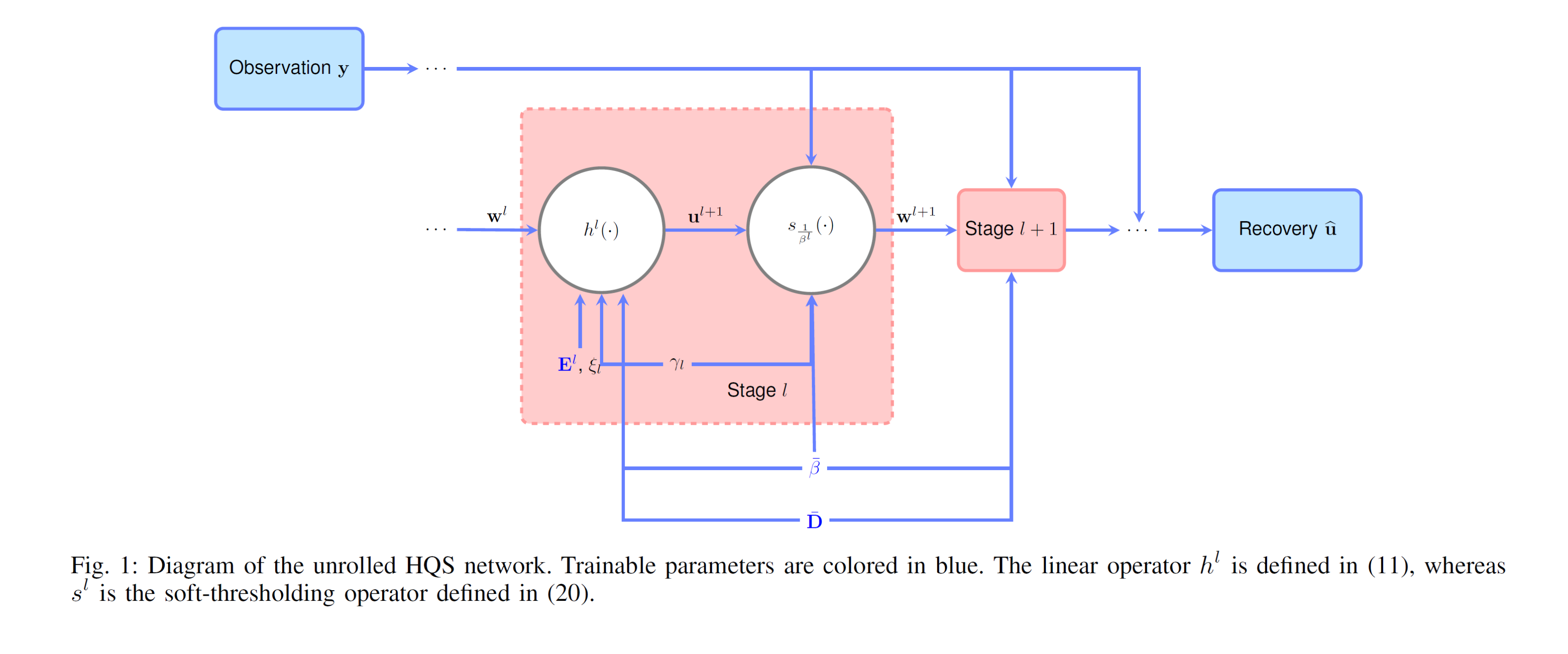
Theorems
Therorem 1 (Convergence result):
For a fixed
Therorem 2 (Convergence rate):
Let
Results
Figure. Visual comparison over BSD dataset and nonlinear kernels.
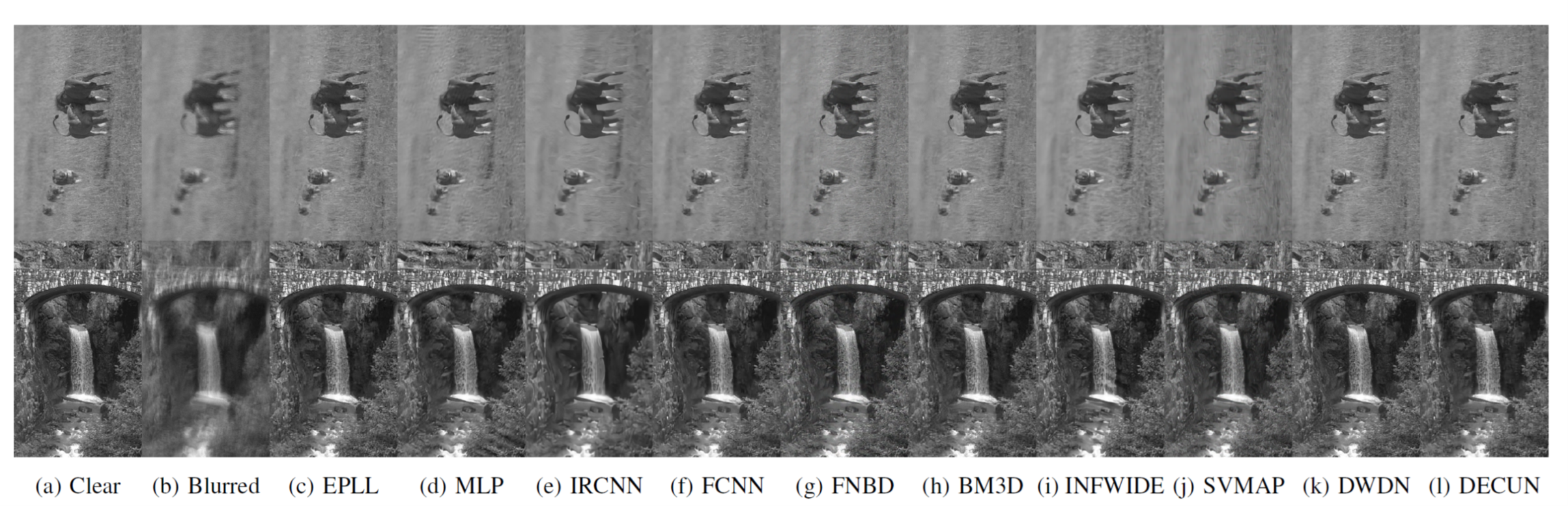
Figure. Visual comparison over BSD dataset and nonlinear kernels.
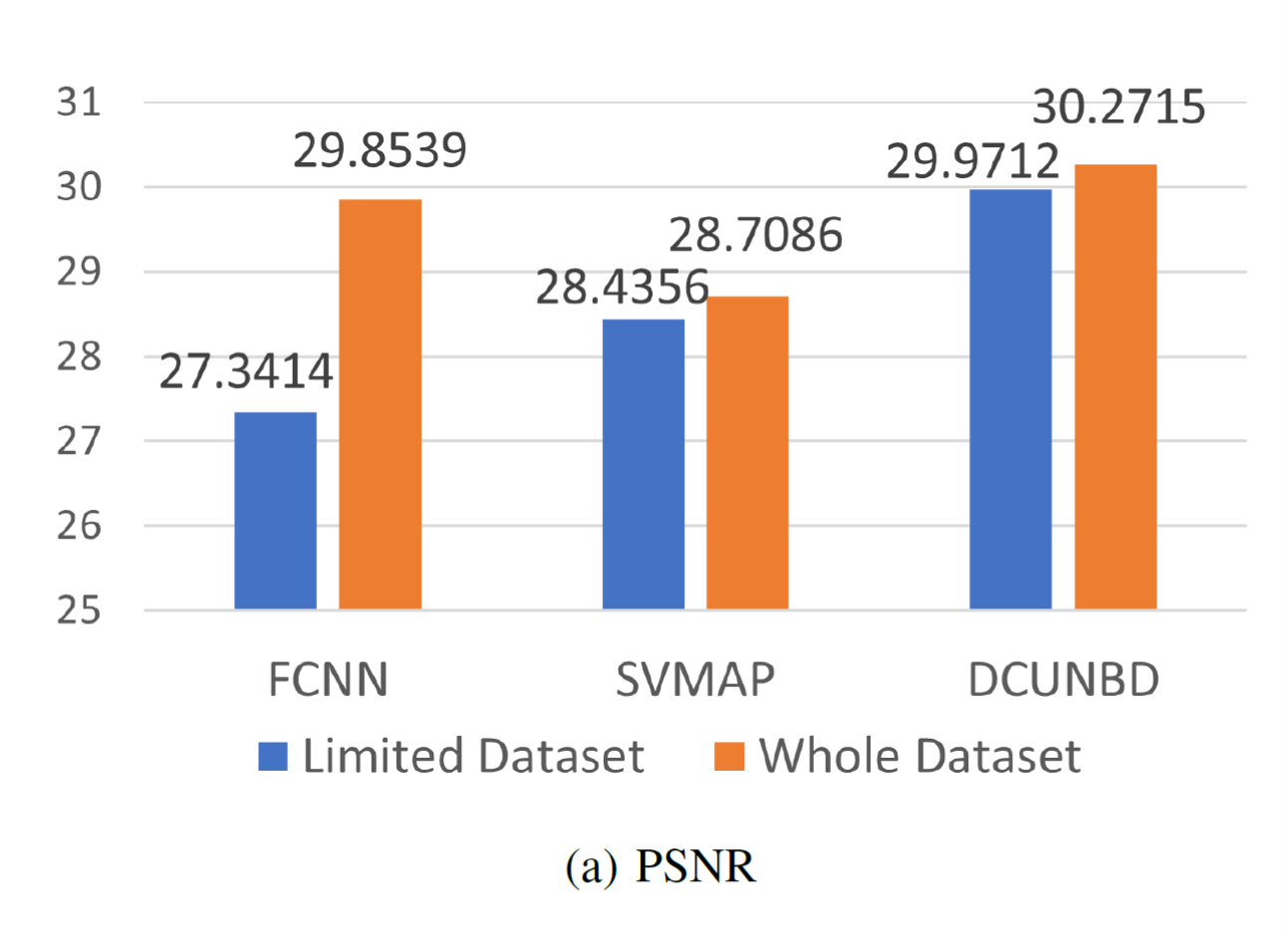
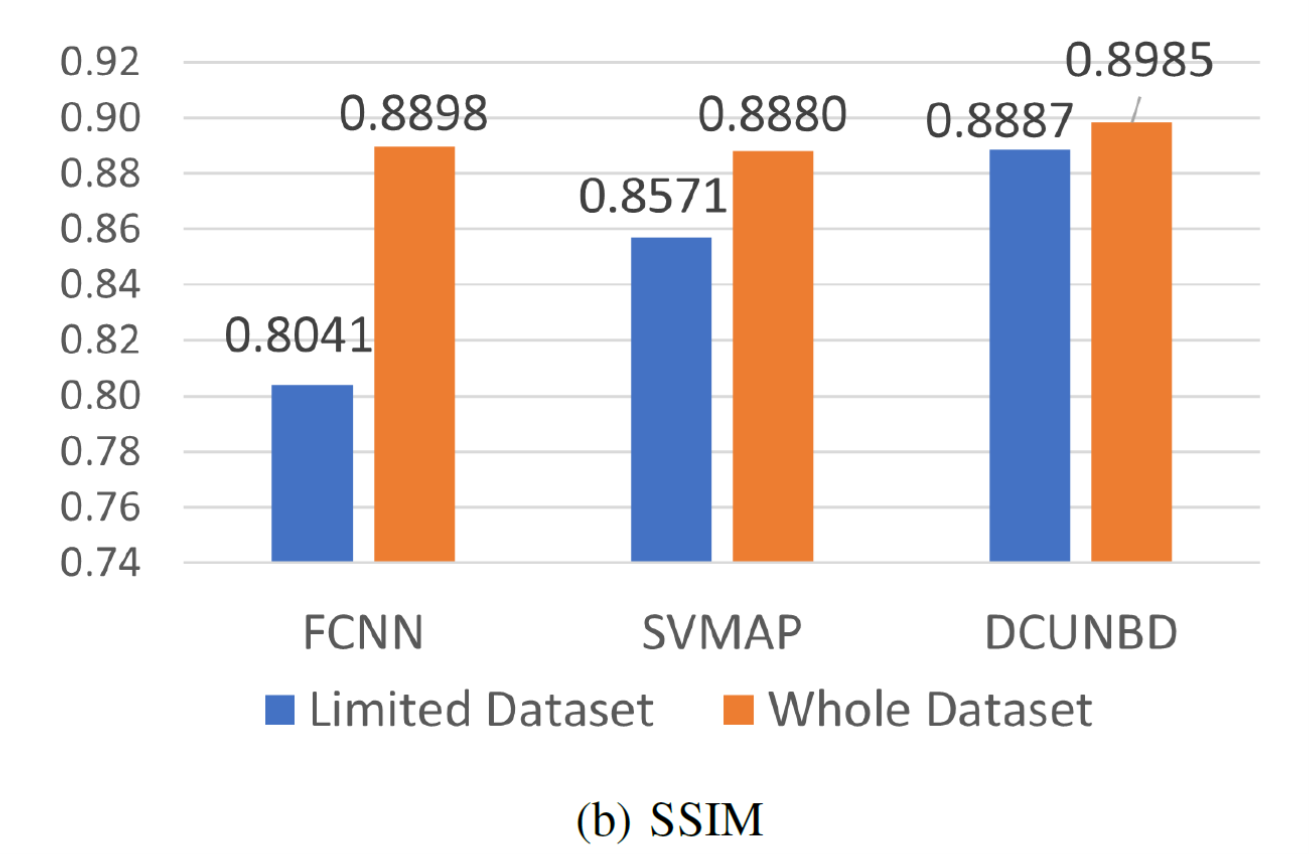
Figure. Performance evaluation in a limited training set-up
Related Publications
Zhao Y, Li Y, Zhang H, Monga V, Eldar YC. Deep, convergent, unrolled half-quadratic splitting for image deconvolution. submitted to IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging. arxiv]
Zhao Y, Li Y, Zhang H, Monga V, Eldar YC. A convergent neural network for non-blind image deblurring. in 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) 2023 Oct 8 (pp. 1505-1509). IEEE. [IEEE]
All rights reserved Ⓒ iPAL 2019